How to analyze SQL queries on a MySQL server
Performance bottlenecks in web applications are frequently caused by inefficient SQL queries. Optimizing these SQL queries is often the most cost-effective way to improve system speed, stability, and scalability.
Here is how to identify and analyze problematic queries on a MySQL server.
1. Identify slow queries
Attention: enable general queries log only for a couple of minutes, this can affect performance on a production server.
2. Analyze slow queries to identify the bottleneck
From the slow query log, we'll have a list of queries that are slower than 2 seconds.
At this step, we should try to understand why they are so slow. We can use the EXPLAIN command from MySQL to achieve this.
Assume we have the following slow query:
just add EXPLAIN in front of the qury like this:
Will return result like this:
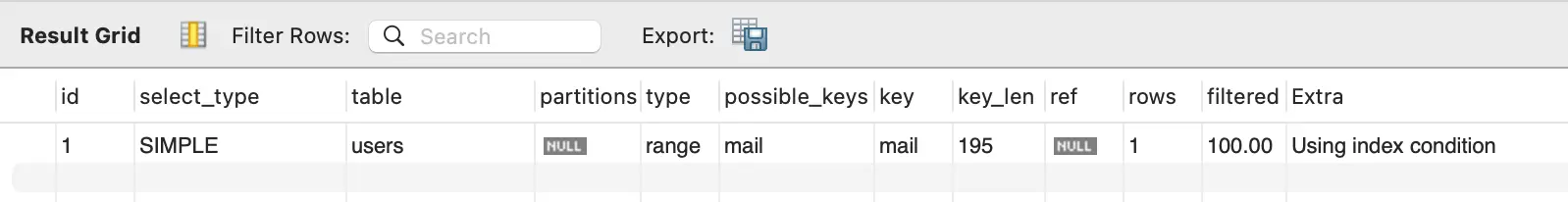
Key Columns to Analyze:
type: This indicates how MySQL joins tables.
key: The index MySQL decided to use. If this is NULL, no index is being used.
rows: The estimated number of rows MySQL believes it must examine to execute the query. Lower is better.
Extra: Look for warnings here.
Using filesort: MySQL is doing an extra pass to sort data (slow).
Using temporary: MySQL is creating a temporary table to hold intermediate results (very slow).